[ad_1]
More than the past 10 several years, researchers led by Fu Qiaomei from the Institute of Vertebrate Paleontology and Paleoanthropology (IVPP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) have applied historical DNA (aDNA) technology to unearth the record of historic human populations, particularly those people in East Asia.
As component of their energy, the scientists reconstructed the complete genome of two extinct groups of archaic humans—Neanderthals and Denisovans mapped the history of world inhabitants migrations and interactions uncovered the genetic structure of the oldest East Asians uncovered adaptive genetic alterations in East Asian Ice Age populations and traced the formation of population designs in northern and southern China as well as the origin of the Austronesian population in southern China.
Just lately, Fu’s workforce reviewed the record of aDNA technological development, talked over current specialized bottlenecks and options, and assessed the long term of the know-how.
The examine was published in Cell on July 21.
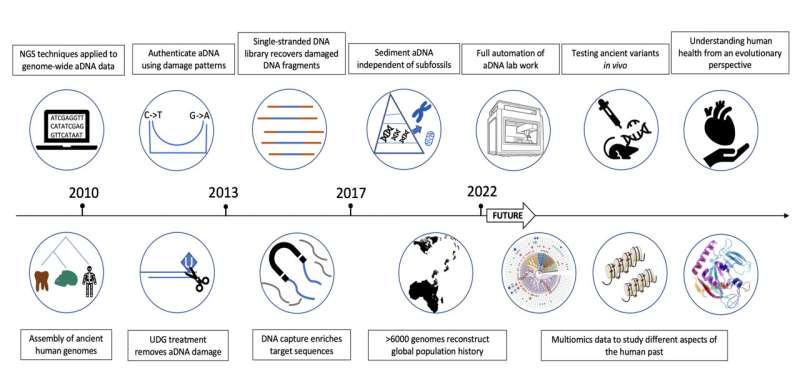
A critical technological progress talked over in the examine is higher-throughput sequencing, which is a method for swiftly sequencing substantial amounts of DNA. It can theoretically sequence all DNA molecules in a sample.
Right before large-throughput sequencing grew to become commonplace, the aDNA discipline relied on polymerase chain response (PCR) methods to sequence a few unique DNA fragments. Researchers could only extract a very confined quantity of DNA facts with this know-how and experienced trouble distinguishing real aDNA from contaminant DNA.
To complement advances in sequencing, aDNA scientists have also designed enhanced approaches of DNA library development to far better reflect the qualities of aDNA. Among these methods, partial uracil-DNA glycosylase (UDG) remedies and single-stranded DNA library construction are two of the most critical. Partial UDG remedy not only preserves section of the DNA problems signal at DNA fragment strategies but also eliminates most aDNA problems throughout the rest of the molecule. This strategy improves the precision of aDNA sequencing success though preserving aDNA capabilities expected for validation. Single-stranded DNA library construction lets the direct sequencing of ruined and denatured DNA fragments that might be dropped in regular modern DNA library development methods.
Improvements in library development have minimal efficacy, nonetheless, considering that aDNA samples typically incorporate a substantial total of environmental DNA. As a result, beneficial endogenous aDNA sequences typically account for significantly less than 1% of the ensuing sequences. To tackle this challenge, researchers have utilized DNA capture technology to the aDNA discipline by creating DNA and RNA probes with sequences very similar to their targets. Immediately after incorporating the probes to sample extracts, the concentrate on aDNA binds to the probes and is then fished out from the massive total of environmental DNA. This engineering is commonly used in historical human genome analysis. Now, more than two-thirds of ancient human genome facts occur from knowledge captured employing the 1240k probe established.
DNA seize technology not only significantly increases the performance of aDNA sequencing it also permits recovery of usable information from samples that would if not be too degraded for evaluation.
A lot more just lately, aDNA scientists have pushed the envelope even more by extracting aDNA directly from soil (i.e., sediment). This technology has been used to samples from the Denisova and Baishiya caves, making it attainable to get well DNA from historic humans who lived tens of hundreds of several years back.
Inspite of its fruitful results, however, the examine of aDNA has constantly been very difficult. aDNA itself is hugely vulnerable to contamination, and experiments involving aDNA are really delicate. In the previous, aDNA extraction and library design ended up practically solely dependent on manual operations. Not too long ago, a few laboratories all around the world have begun to combine some aDNA techniques with totally automatic, pipetting robot platforms. On the other hand, at existing, pre-processing of samples nevertheless involves guide steps. How to integrate this time-consuming and labor-intensive operate into an automatic program is the next problem for aDNA experimental technology.
The application of aDNA engineering goes much beyond the ancient human genome, of course. Paleomolecular exploration also covers essential subject areas these kinds of as tracing ancient epidemics and symbiotic microbial evolution by historic microbial facts working with ancient epigenetic information to discover the interaction among historical animals and the surroundings and working with historic proteins to discover human evolution more than long time intervals, which include how aDNA influences the physiology and health of modern-day people.
aDNA is time-stamped genetic information and facts that records the evolution and adaptation of human beings about tens of 1000’s of many years. We now know from aDNA study that many critical useful genetic haplotypes derive from archaic human populations. These genes are included in innate immunity, lipid rate of metabolism, high-altitude survivability, and skin shade. Even so, the features of most genetic variants identified by aDNA experiments have not however been determined.
In the future, scientists may perhaps use the most current gene-modifying technological know-how to assemble aDNA animal versions that reveal the perform of a lot of unknown aDNA variants. This will help us far better have an understanding of how contemporary-working day human physiology and overall health have been afflicted by the genetic inheritance from our ancient forebears.
Decoding human historical past with historic DNA
Fu Qiaomei et al, Evolving historic DNA techniques and the upcoming of human historical past, Cell (2022). DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2022.06.009. www.mobile.com/cell/fulltext/S0092-8674(22)00714-
Citation:
Scientists chart advancements in historic DNA know-how (2022, July 21)
retrieved 22 July 2022
from https://phys.org/news/2022-07-advancements-historic-dna-know-how.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any good dealing for the function of personal analyze or study, no
part could be reproduced without the published permission. The material is presented for information needs only.
[ad_2]
Supply url





More Stories
US AI Industry Growth Surges: What You Need to Know
Inside the AI Boom: How the US is Leading AI Development
3 Major Advantages Of Technological Innovations