[ad_1]
Though blood clotting is important to protect against blood decline and for our immunity, coagulation also can lead to health challenges and even demise. Now, one in four people worldwide dies from ailments and ailments induced by blood clots. In the meantime, anticoagulants made use of to lessen dangers can also result in important challenges, this sort of as uncontrolled bleeding.
Now, a new biomolecular anticoagulant system invented by a workforce led by UNC Charlotte researcher Kirill Afonin retains assure as a innovative progression around the blood thinners now employed through surgeries and other procedures. The team’s discoveries are reported in the journal Nano Letters, 1st readily available on the net on July 5.
“We visualize the makes use of of our new anticoagulant platform would be through coronary artery bypass surgeries, kidney dialysis, and a variety of vascular, surgical and coronary interventions,” Afonin reported. “We are now investigating if there are opportunity potential purposes with most cancers remedies to avoid metastasis and also in addressing the wants of malaria, which can bring about coagulation concerns.”
The paper shares the most current success from a few a long time of collaboration among the scientists with the Frederick National Laboratory for Most cancers Investigation (Nanotechnology Characterization Laboratory), University of São Paulo in Brazil, The Pennsylvania Condition University, and Uniformed Services University of the Well being Sciences.
“All this resulted in a large intercontinental and interdisciplinary energy to acquire a fully new technology that we feel could revolutionize the subject and be picked up by other places of wellness exploration,” Afonin said.
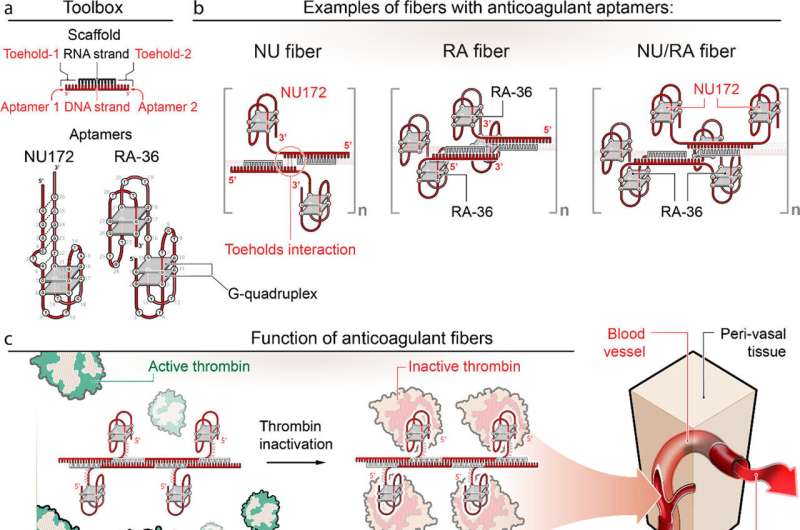
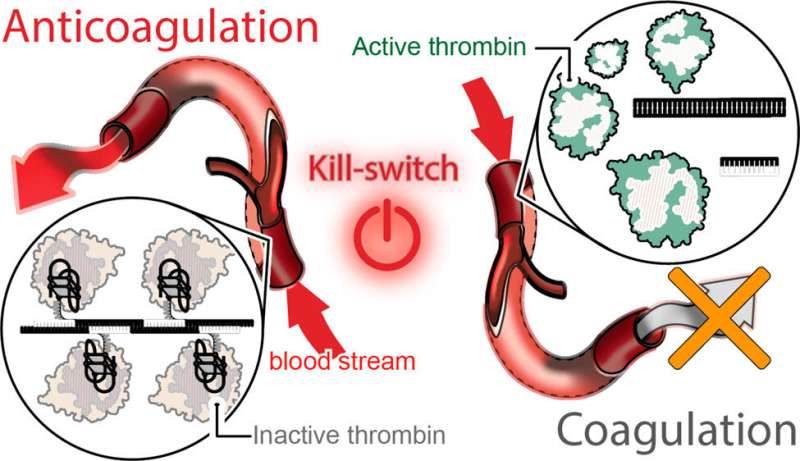
The team’s technology turns to programmable RNA-DNA anticoagulant fibers that, when injected into the bloodstream, kind into modular constructions that connect with thrombin, which are the enzymes in blood plasma that cause blood to clot. The technology permits the structures to prevent blood clotting as it is wanted, then be swiftly removed from the human body by the renal program the moment the get the job done is completed.
The fiber buildings use aptamers, short sequences of DNA or RNA developed to especially bind and inactivate thrombin.
“Instead of owning a one compact molecule that deactivates thrombin,” Afonin stated, “we now have a somewhat massive framework that has hundreds of the aptamers on its surface area that can bind to thrombin and deactivate them. And mainly because the construction gets greater, it will circulate in the bloodstream for a considerably more time time than conventional choices.”
The extended circulation in the bloodstream lets for a solitary injection, instead of various doses. The style and design also decreases the focus of anticoagulants in the blood, resulting in much less strain on the body’s renal and other systems, Afonin claimed.
This technological innovation also introduces a novel “destroy-swap” mechanism. A 2nd injection reverses the fiber structure’s anticoagulant purpose, letting the fibers to metabolize into components that are little, harmless, inactive and quickly excreted by the renal procedure.
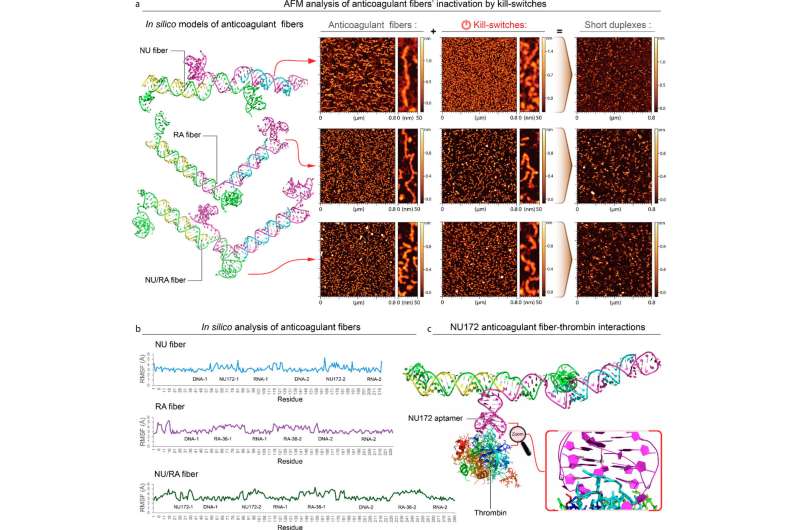
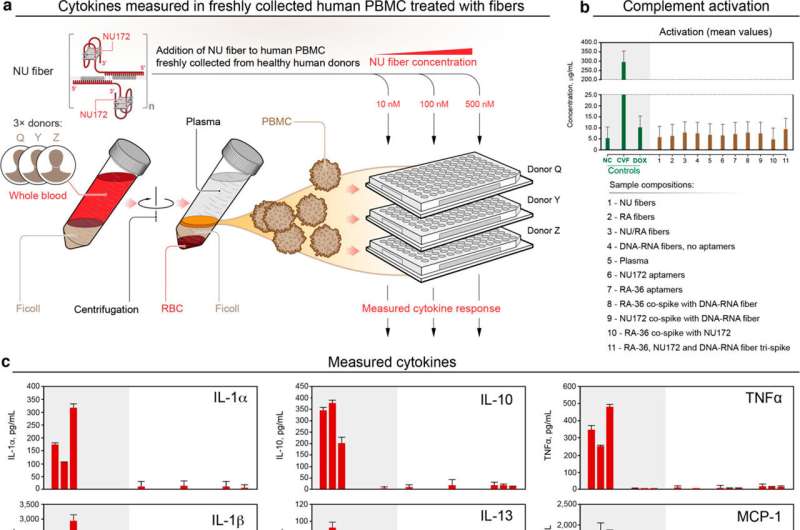
The complete process can take put outdoors the mobile, via extracellular interaction with the thrombin. The researchers be aware that this is vital as immunological reactions do not seem to take place, based on their intensive reports.
The team has analyzed and validated the platform utilizing computer system designs, human blood and several animal types. “We carried out proof-of-notion reports making use of freshly gathered human blood from donors in the U.S. and in Brazil to address a opportunity inter donor variability,” Afonin mentioned.
The technological know-how may give a basis for other biomedical programs that demand communication by means of the extracellular surroundings in individuals, he stated. “Thrombin is just one prospective software,” he said. “Regardless of what you want to deactivate extracellularly, without the need of moving into the cells, we think you can. That probably usually means that any blood protein, any mobile floor receptors, possibly antibodies and toxic compounds, are probable.”
The method permits the design of structures of any condition preferred, with the get rid of change system intact. “By changing the form, we can have them go into diverse sections of the body, so we can change the distribution,” Afonin reported. “It will get an excess layer of sophistication of what it can do.”
Although the software is sophisticated, output of the buildings is fairly effortless. “The shelf everyday living is amazingly superior for these formulations,” Afonin explained. “They’re really stable, so you can dry them, and we anticipate they will keep for several years at ambient temperatures, which tends to make them pretty accessible to economically challenged locations of the world.”
While the researchers’ work so far has relevance for short-term applications, such as in surgeries, they hope to possibly extend their research into maintenance situations, such as with medications that patients with heart conditions take.
The potential for saving lives and improving health care is a motivator for the team, as is inventing something new, Afonin said. “We can learn from nature, but we have built something that has never been introduced before,” he said. “So, we develop and build all these platforms de novo—from scratch. And then we can explain through our platforms what we want nature—or our bodies—to do and our bodies understand us.”
UNC Charlotte’s Office of Research Commercialization and Development is working closely with Penn State to patent and bring this new technology to market.
New test method to standardize immunological evaluation of nucleic acid nanoparticles
Weina Ke et al, Locking and Unlocking Thrombin Function Using Immunoquiescent Nucleic Acid Nanoparticles with Regulated Retention In Vivo, Nano Letters (2022). DOI: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.2c02019
Citation:
Team invents new anticoagulant platform, offering hope for advances for heart surgery, dialysis, other procedures (2022, July 14)
retrieved 18 July 2022
from https://phys.org/news/2022-07-team-anticoagulant-platform-advances-heart.html
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no
part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.
[ad_2]
Source link





More Stories
US AI Industry Growth Surges: What You Need to Know
Inside the AI Boom: How the US is Leading AI Development
3 Major Advantages Of Technological Innovations